Make effective ddos attack
Make effective ddos attack
Content
- How to acquire enough bandwidth
- Common DDoS toolkits
- How to bypass a CDN and locate the origin
- Useful websites
How to acquire enough bandwidth
You’ll need to make use of many free services similar to EC2. Prepare lots of fingerprint browsers or virtual machines.
For example, I can run 16 virtual machines at once.
What is a fingerprint browser? (generated by GPT‑4 with Bing) A fingerprint browser is a specialized browser technology used to identify and track visitors. It lets users log in to multiple accounts on the same machine without linking them. This anti-association feature is mainly used in cross-border e-commerce and social media marketing. It keeps data isolated and allows you to modify info like timezone or address.
Now prepare 16 Google accounts and 16 Microsoft accounts to log in. Sign in to common developer websites.
Places where you can get free compute
Common DDoS toolkits
webBenchmark
usage
webBenchmark -c [COUNT] -s [URL] -r [REFERER]
-c int
concurrent routines for download (default 16)
-r string
referer url
-s string
target url (default "https://baidu.com")
-i string
custom ip address for that domain, multiple addresses automatically will be assigned randomly
-H http header pattern
http header pattern, use Random with number prefix will generate random string, same key will be overwritten
-f string
randomized X-Forwarded-For and X-Real-IP address
-p string
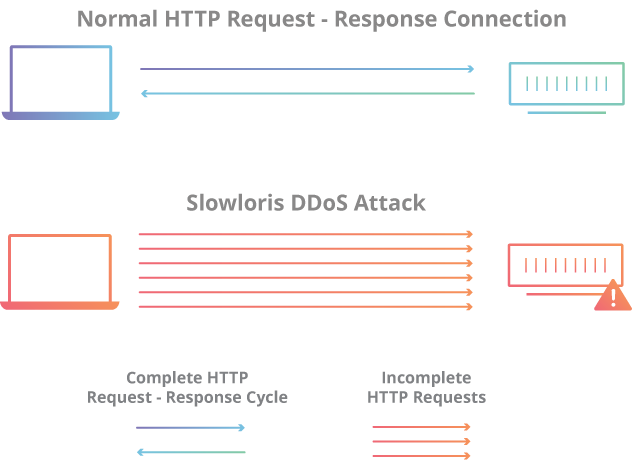
post contentslowloris
what is slowloris: cloudflare link

How to bypass a CDN and locate the origin
Use multi-location ping
Bruteforce all third-level domains (ksubdomain)
ksubdomain is a stateless subdomain brute-forcing tool for Windows/Linux/Mac. It can blast DNS queries very quickly—up to 300k/s on Mac and Windows and 1.6M/s on Linux.
Sending and receiving are decoupled from the system, so even with high concurrency it doesn’t exhaust file descriptors.
Use --test to check your local sending rate. Actual throughput depends on your network. The tool simplifies this with the -b parameter—for example -b 5m—to throttle packets automatically.
Check historical DNS records
The IP used before a domain was behind a CDN is often the real origin IP.
Tool
https://github.com/zidansec/CloudPeler
This tool serves to find the original IP behind websites that have been protected by CloudFlare, the information generated can be useful for further penetration. The information generated by this tool is as follows.
- CloudFlare IP
- CloudFlare NS1
- CloudFlare NS2
- Real IP
- Hostname
- Organization
- Address (Country, City, Region, Postal Code)
- Location
- Time Zone
Other tricks
Check whether HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR is empty; if not, treat it as the IP address, otherwise use REMOTE_ADDR.
If you can upload files to the server, add code like this:
Request.ServerVariables("LOCAL_ADDR") gets the server IP
Request.ServerVariables("REMOTE_ADDR") gets the client IP (possibly a proxy)
request.ServerVariables("HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR") gets the real client IP
Have the server initiate a connection to us (including RSS mail subscriptions)
Directly visiting a CDN-protected domain hits the CDN first. But if we make the server connect back to us, we can quickly learn its real IP.
Most sites send email directly from their own servers. If the server has sendmail installed, registering will trigger a message. Check the email headers to see the real IP, which is often in the same subnet as the main site. Probe port 80 hosts in that range.
Useful websites
isitdownrightnow
https://www.isitdownrightnow.com/
Check whether a site is truly reachable.
Google Public DNS
Look up DNS records such as A, AAAA, CNAME, NS and MX.
Fofa
Internet-wide scanning engines work by using many servers around the clock to probe everything exposed online—every IP address, open port and service, and the response to each request.
Most websites have an icon. These engines also collect icon hashes. Calculate your site’s icon hash and search it on FOFA—if another IP uses the same hash, that’s probably your real address.